OPT (Optical Projection Tomography) Scanning
Introduction
Optical Projection Tomography (OPT) is a microscopic imaging technique which captures 3D data directly without the need to physically section the specimen.
The specimen remains undamaged and can be used for further analysis including microtome sectioning for high-resolution microscopy and detailed in situ staining (e.g. hybridisation or immunohistochemistry).
The development of OPT has allowed a significant improvement in the digital recontruction of the models. Where the embryos are embedded in wax, the histological process will cause some distortion as the sections are floated out onto heated water. This distortion causes difficulty with the alignment during computational reconstruction. The OPT scan is used as a scaffold that retains the shape of the embryo, so that the histology sections can be aligned more accurately.
More information about OPT and how it works can be found
on the OPT microscopy web pages.Protocol
Pre OPT preparation
Specimens are prepared in agarose for scanning as described in Embryo collection - Agarose for OPT.
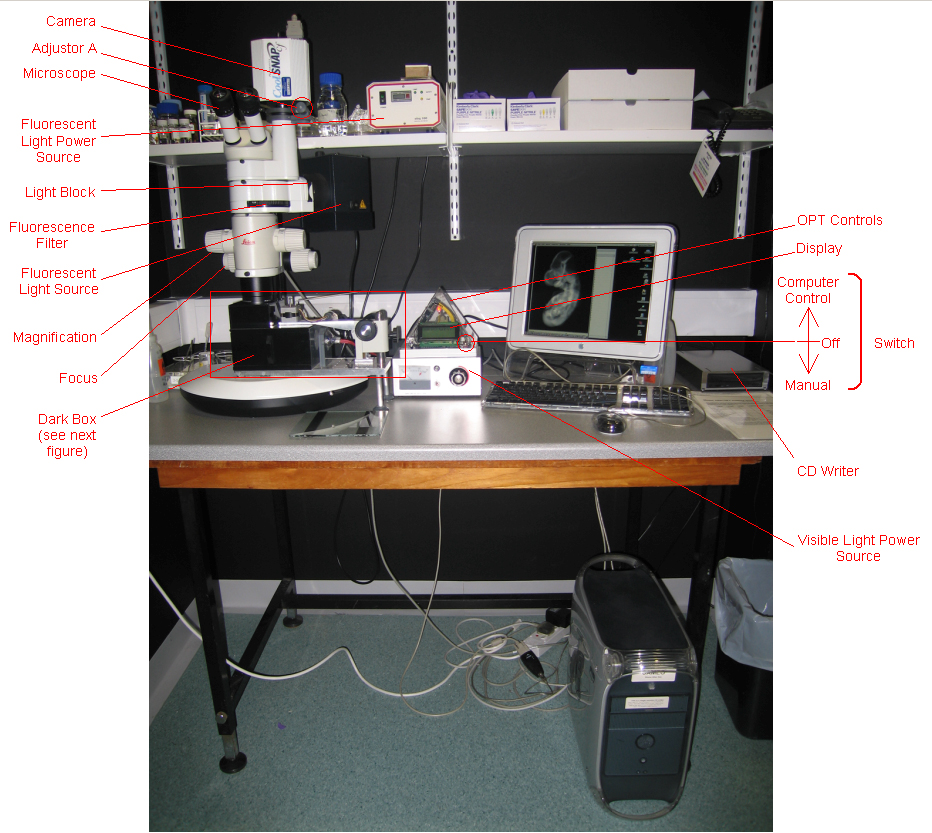
OPT apparatus
Prepared specimens are set in the OPT apparatus
| OPT apparatus |
 |
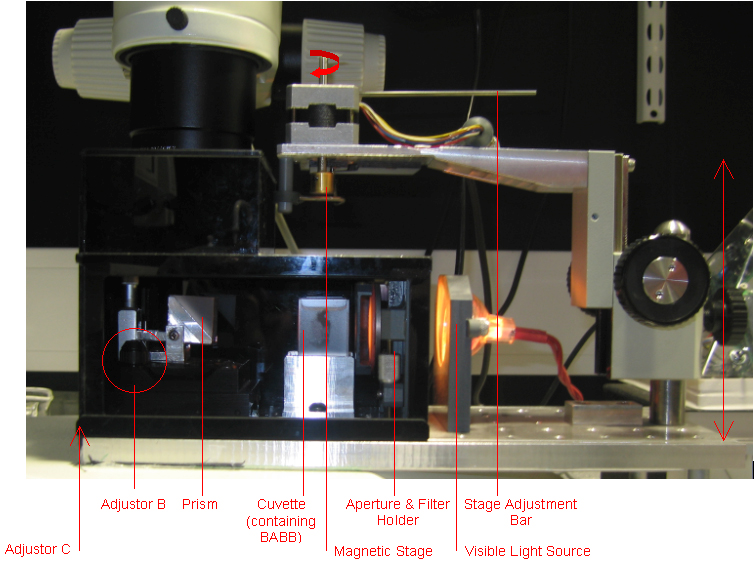
| OPT darkbox containing cuvette |
 |
Calibration of the OPT apparatus
Calibration of the apparatus may be required. The OPT computer performs calibration measurements and instructs the operator if adjustments are necessary.
OPT scanning
The mounted specimen is placed onto a magnetic stage and lowered into a cuvette containing BABB.
The specimen is properly positioned to identify the centre of rotation.
The camera is focused accurately on the specimen.
Exposure time is set.
The scanning operation is started. The OPT computer controls the scanning process.
When the scan is complete, the scanned data is written to disc.
Post OPT specimen preparation
The specimen is prepared for histology sectioning.